|
The coastal defences of the 18th century are divided into three groups: the coastal batteries, coastal redoubts and coastal entrenchments and later the fougass was also added. The building of coastal batteries was in what could be said as an extension of the coastal defences began in the 17th century. The early 18th century saw a new enthusiasm for coastal defences, after the brief interest that had erupted in the first half of the previous century (1700s). The concept of a chain of towers around the coast was a Spanish idea. On the other hand, the concept of coastal batteries was a French idea.
All over their possessions the French built these types of fortifications. In one of their possessions, Quebec, they built an extensive number of coastal batteries in the vicinity of the city. These coastal batteries succeeded in resisting the British attempts to disembark soldiers in their area, while those built in Malta were overwhelmed immediately, partially due to Hospitaller traitors and lack of enthusiasm in the maintenance of the defences. When Bonaparte decided to invade the Maltese islands he knew about this fact. (For those Maltese readers they can see my article about the fortifications in Mellieha of the 18th century Fortifikazzjonijiet fil-Mellieha tas-seklu tmintax: batteriji, ridotti u truncieri: Xebh bejn is-sistema ta difiza li nbniet Malta, ma dawk li nbnew fl-imperu Franciz matul dan iz-zmien in Imperial Band Club Mellieha Festa tal-Vitorja 2005).1 In 1714 two French military experts employed by the Hospitallers, Bernard Fontet and Jacques de Camus d’Arginy emphasised on the importance of building coastal defences at Marsaxlokk and Marsascala. On the request of the Hospitaller Congregation of War they later expended their plan to the whole Island including the various bays which are found in Mellieha. The Order began constructing coastal batteries in various parts of the Island including in Mellieha, especially on the coast facing Comino. The arrival of Prince Philip de Vendome in 1715 accelerated the process of the building of these coastal fortifications. He was the greatest supporter for the building of the coastal batteries. 2
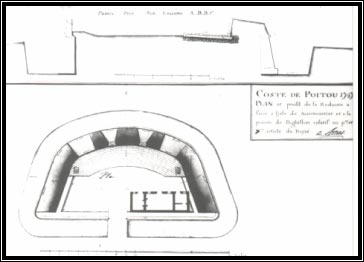
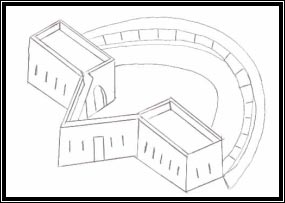
Many knights donated sums of money for the construction of coastal batteries; one of them was Commander Mongontier. Part of his donation was used for the building of a number of these structures in the Mellieha area. The coastal batteries were armed with various calibres of artillery, with the aim of having proper cannon to defend those vulnerable bays. 3 The majority of the coastal batteries were built from 1714 to 1716. Generally, the coastal batteries were built opposite each other in order to defend the bay well. The main model of coastal battery was a semi-circular platform for cannons, two block rooms at the back and a redan in the middle of them. This model of coastal battery was very similar to that built by the French in their colonies. It was also the main type of coastal battery built in the village of Mellieha. A number of coastal towers had also a coastal battery built during this period. The White tower in Mellieha endured a similar process. 4 A group of French military engineers who inspected the coastal defences in 1761 recommended the building of more coastal batteries, but only few of the proposed batteries were eventually built. The coastal batteries were not locked during the year and it was manned only during the summer which was the most appropriate time for an invasion. 5 |
||||||
|
|
||||||
References:
Researched and Written by: Charles Debono B.A.(Hons) History |
||||||
Maltaserv Bannerlink